Connect Kubectl
In Kubernetes, the configuration for accessing your cluster is in a format known as kubeconfig, which is stored as a file. It contains details such as cluster API server addresses and access credentials or a command to obtain access credentials from a kubectl credential plugin. In general, treat a kubeconfig as sensitive data. Tools like kubectl use the kubeconfig to connect and authenticate to a cluster and perform operations on it. Learn more about kubeconfig and kubectl on kubernetes.io.
Tools
In this guide, we reference the following tools:
- kubectl: Command-line tool for running commands against Kubernetes clusters. It allows you to control various aspects of your cluster, such as creating or modifying resources, viewing resource status, and debugging your applications.
- kubelogin:
kubectlcredential plugin used for OIDC authentication, which is required for the (OIDC)Gardencluster kubeconfig - gardenlogin:
kubectlcredential plugin used forShootauthentication assystem:masters, which is required for the (gardenlogin)Shootcluster kubeconfig - gardenctl: Optional. Command-line tool to administrate one or many
Garden,SeedandShootclusters. Use this tool to setupgardenloginandgardenctlitself, configure access to clusters and configure cloud provider CLI tools.
Connect Kubectl to a Shoot Cluster
In order to connect to a Shoot cluster, you first have to install and setup gardenlogin.
You can obtain the kubeconfig for the Shoot cluster either by downloading it from the Gardener dashboard or by copying the gardenctl target command from the dashboard and executing it.
Setup Gardenlogin
Prerequisites
- You are logged on to the Gardener dashboard.
- The dashboard admin has configured OIDC for the dashboard.
- You have installed kubelogin
- You have installed gardenlogin
To setup gardenlogin, you need to:
Download Kubeconfig for the Garden Cluster
- Navigate to the
MY ACCOUNTpage on the dashboard by clicking on the user avatar ->MY ACCOUNT. - Under the
Accesssection, download the kubeconfig.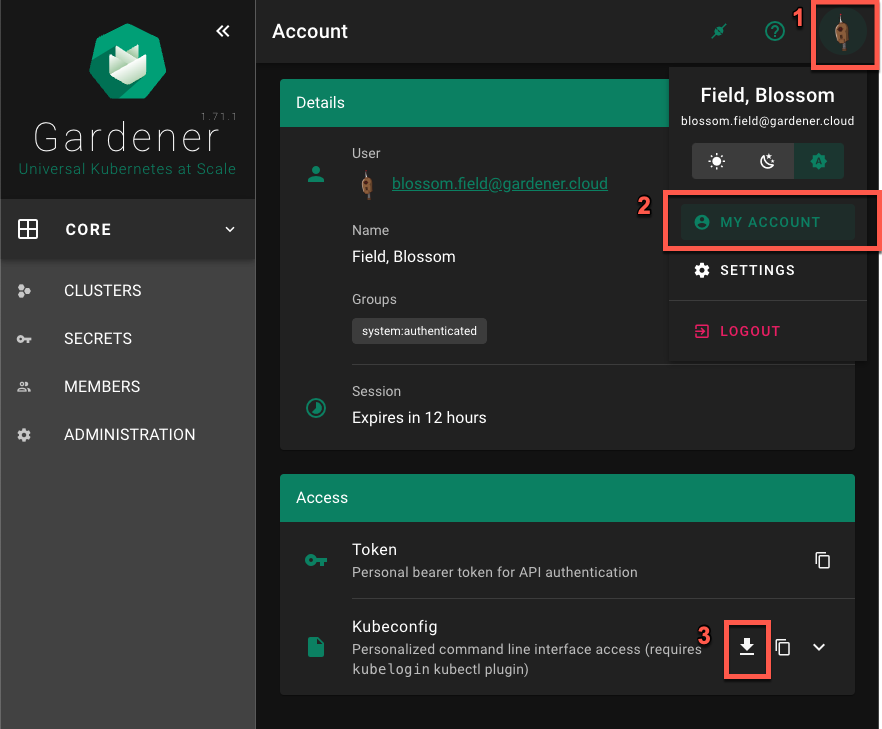
Configure Gardenlogin
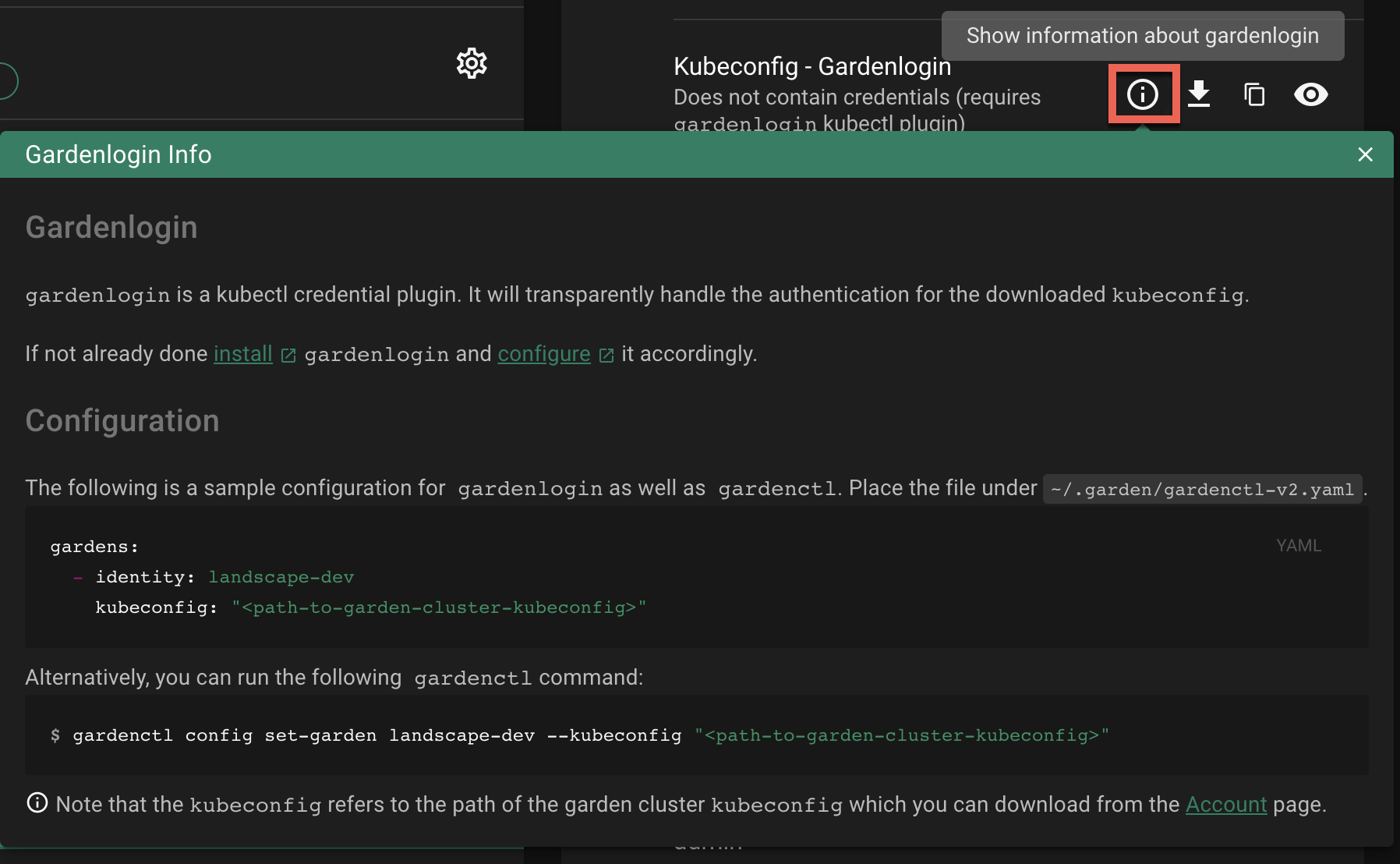
Configure gardenlogin by following the installation instruction on the dashboard:
- Select your project from the dropdown on the left
- Choose
CLUSTERSand select your cluster in the list. - Choose the
Show information about gardenlogininfo icon and follow the configuration hints.
IMPORTANT
Use the previously downloaded kubeconfig for the Garden cluster as the kubeconfig path. Do not use the gardenlogin Shoot cluster kubeconfig here.
Download and Setup Kubeconfig for a Shoot Cluster
The gardenlogin kubeconfig for the Shoot cluster can be obtained in various ways:
- Copy and run the
gardenctl targetcommand from the dashboard - Download from the Gardener dashboard
Copy and Run gardenctl target Command
Using the gardenctl target command you can quickly set or switch between clusters. The command sets the scope for the next operation, e.g., it ensures that the KUBECONFIG env variable always points to the current targeted cluster.
To target a Shoot cluster:
Copy the
gardenctl targetcommand from the dashboard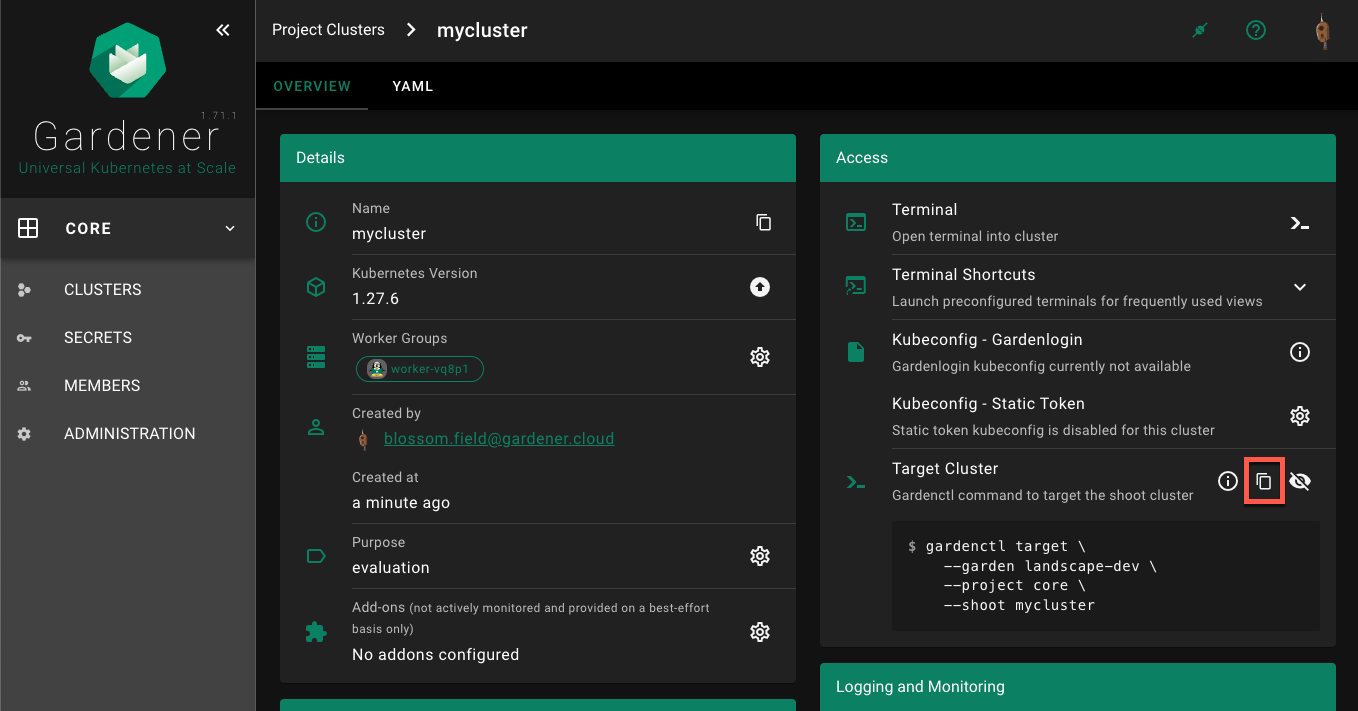
Paste and run the command in the terminal application, for example:
$ gardenctl target --garden landscape-dev --project core --shoot mycluster
Successfully targeted shoot "mycluster"Your KUBECONFIG env variable is now pointing to the current target (also visible with gardenctl target view -o yaml). You can now run kubectl commands against your Shoot cluster.
$ kubectl get namespacesThe command connects to the cluster and list its namespaces.
KUBECONFIG Env Var not Setup Correctly
If your KUBECONFIG env variable does not point to the current target, you will see the following message after running the gardenctl target command:
WARN The KUBECONFIG environment variable does not point to the current target of gardenctl. Run `gardenctl kubectl-env --help` on how to configure the KUBECONFIG environment variable accordinglyIn this case you would need to run the following command (assuming bash as your current shell). For other shells, consult the gardenctl kubectl-env --help documentation.
$ eval "$(gardenctl kubectl-env bash)"Download from Dashboard
Select your project from the dropdown on the left, then choose
CLUSTERSand locate your cluster in the list. Choose the key icon to bring up a dialog with the access options.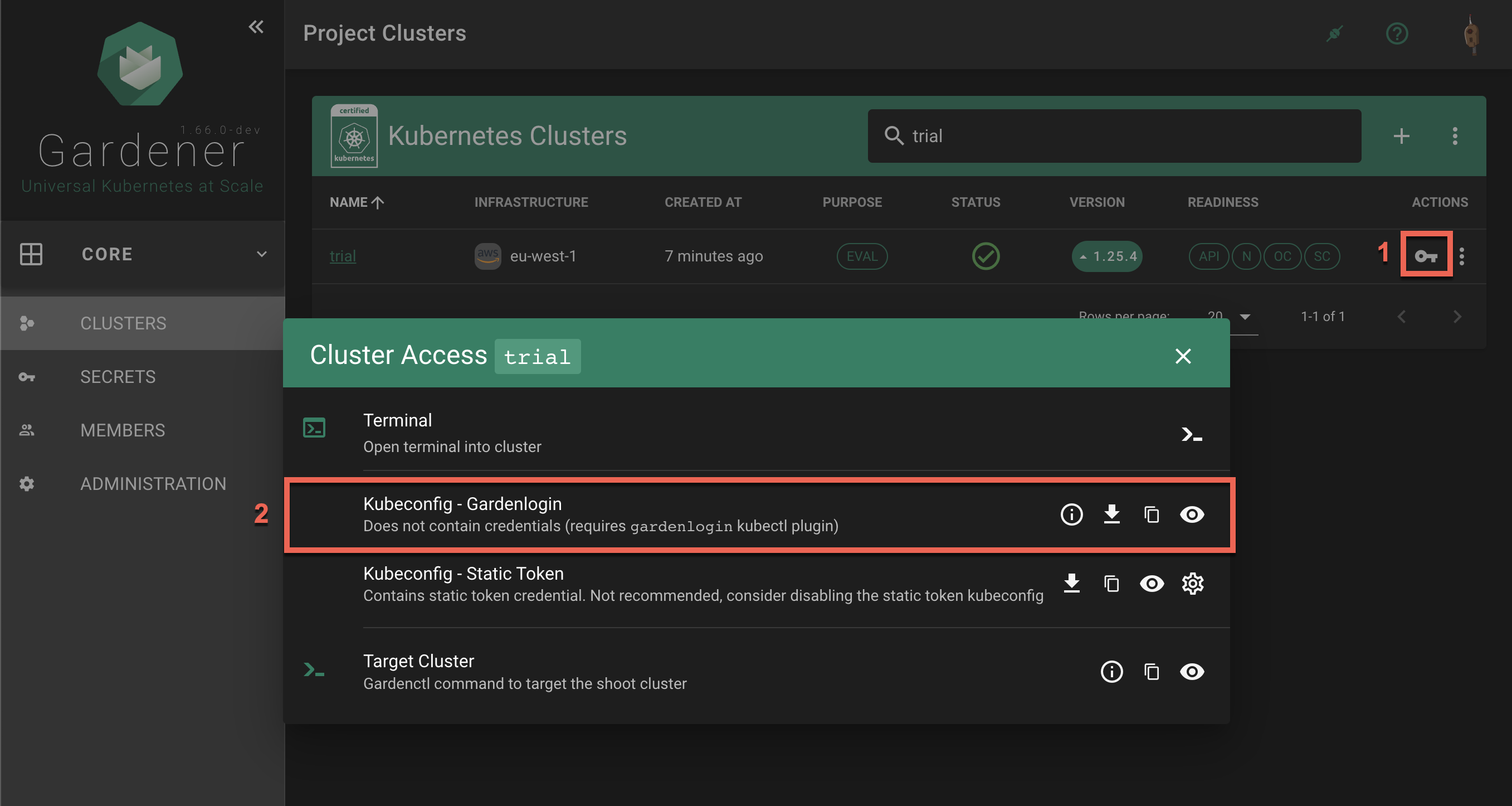
In the
Kubeconfig - Gardenloginsection the options are to show gardenlogin info, download, copy or view thekubeconfigfor the cluster.The same options are available also in the
Accesssection in the cluster details screen. To find it, choose a cluster from the list.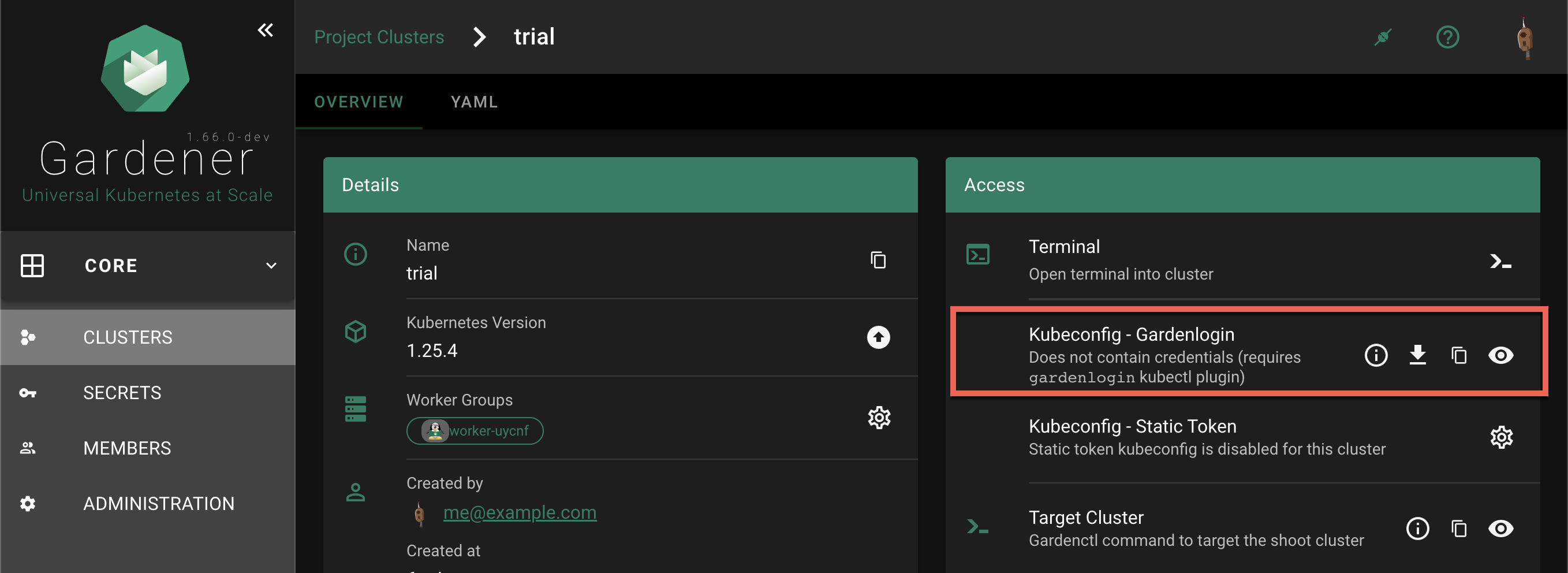
Choose the download icon to download the
kubeconfigas file on your local system.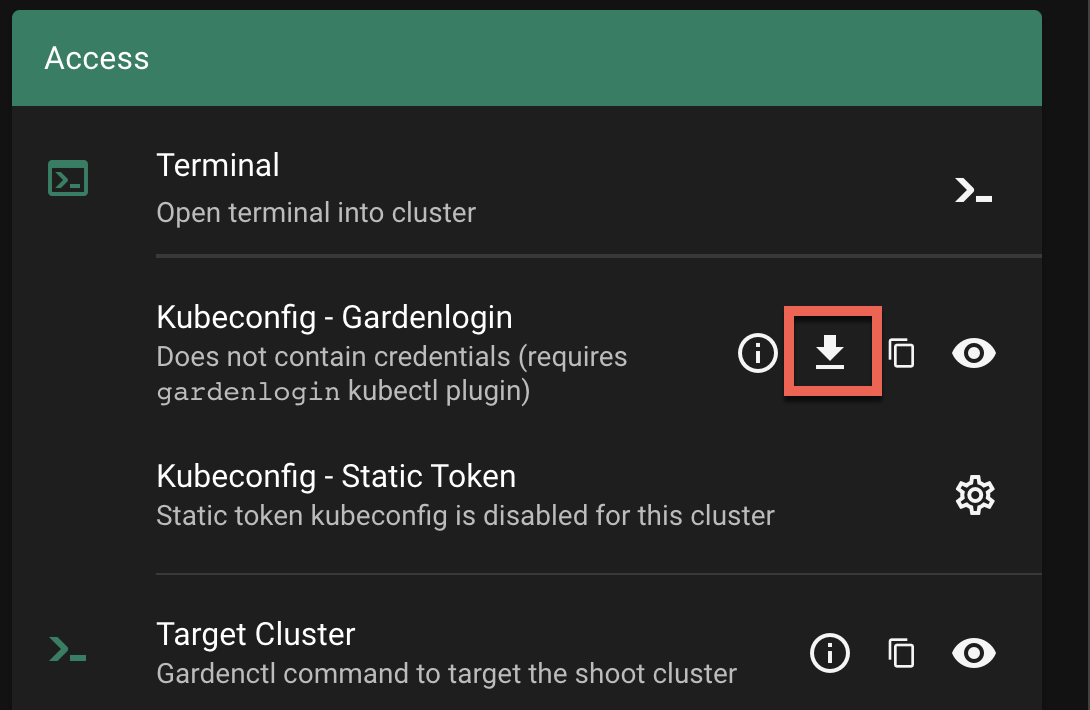
Connecting to the Cluster
In the following command, change <path-to-gardenlogin-kubeconfig> with the actual path to the file where you stored the kubeconfig downloaded in the previous step 2.
$ kubectl --kubeconfig=<path-to-gardenlogin-kubeconfig> get namespacesThe command connects to the cluster and list its namespaces.
Exporting KUBECONFIG environment variable
Since many kubectl commands will be used, it’s a good idea to take advantage of every opportunity to shorten the expressions. The kubectl tool has a fallback strategy for looking up a kubeconfig to work with. For example, it looks for the KUBECONFIG environment variable with value that is the path to the kubeconfig file meant to be used. Export the variable:
$ export KUBECONFIG=<path-to-gardenlogin-kubeconfig>Again, replace <path-to-gardenlogin-kubeconfig> with the actual path to the kubeconfig for the cluster you want to connect to.