Using the AWS provider extension with Gardener as an end-user
The core.gardener.cloud/v1beta1.Shoot resource declares a few fields that are meant to contain provider-specific configuration.
In this document we are describing how this configuration looks like for AWS and provide an example Shoot manifest with minimal configuration that you can use to create an AWS cluster (modulo the landscape-specific information like cloud profile names, secret binding names, etc.).
Accessing AWS APIs
In order for Gardener to create a Kubernetes cluster using AWS infrastructure components, a Shoot has to provide an authentication mechanism giving sufficient permissions to the desired AWS account. Every shoot cluster references a SecretBinding or a CredentialsBinding.
IMPORTANT
While SecretBindings can only reference Secrets, CredentialsBindings can also reference WorkloadIdentitys which provide an alternative authentication method. WorkloadIdentitys do not directly contain credentials but are rather a representation of the workload that is going to access the user's account. If the user has configured OIDC Federation with Gardener's Workload Identity Issuer then the AWS infrastructure components can access the user's account without the need of preliminary exchange of credentials.
IMPORTANT
The SecretBinding/CredentialsBinding is configurable in the Shoot cluster with the field secretBindingName/credentialsBindingName. SecretBindings are considered legacy and will be deprecated in the future. It is advised to use CredentialsBindings instead.
Provider Secret Data
Every shoot cluster references a SecretBinding or a CredentialsBinding which itself references a Secret, and this Secret contains the provider credentials of your AWS account. This Secret must look as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: core-aws
namespace: garden-dev
type: Opaque
data:
accessKeyID: base64(access-key-id)
secretAccessKey: base64(secret-access-key)The AWS documentation explains the necessary steps to enable programmatic access, i.e. create access key ID and access key, for the user of your choice.
WARNING
For security reasons, we recommend creating a dedicated user with programmatic access only. Please avoid re-using a IAM user which has access to the AWS console (human user).
Depending on your AWS API usage it can be problematic to reuse the same AWS Account for different Shoot clusters in the same region due to rate limits. Please consider spreading your Shoots over multiple AWS Accounts if you are hitting those limits.
AWS Workload Identity Federation
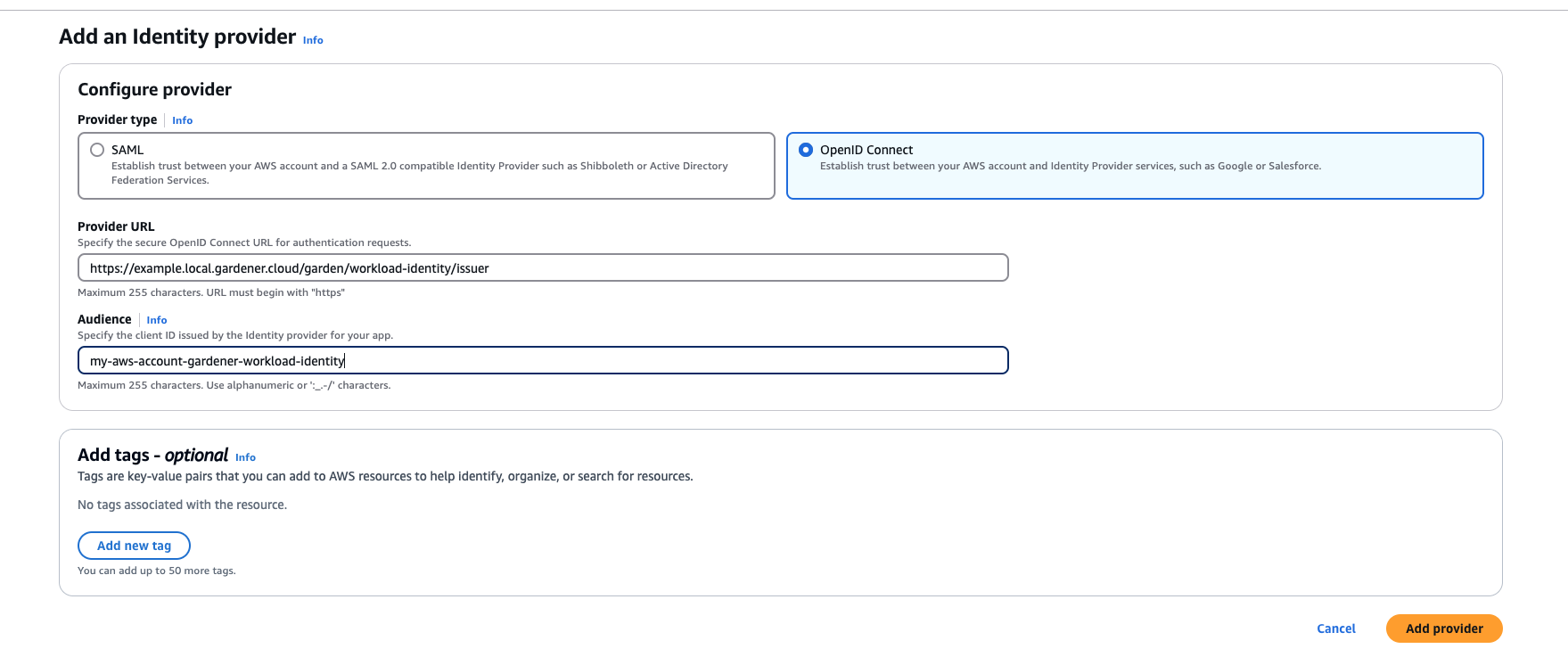
Users can choose to trust Gardener's Workload Identity Issuer and eliminate the need for providing AWS Access Key credentials.
1. Configure OIDC Federation with Gardener's Workload Identity Issuer.
TIP
You can retrieve Gardener's Workload Identity Issuer URL directly from the Garden cluster by reading the contents of the Gardener Info ConfigMap.
kubectl -n gardener-system-public get configmap gardener-info -o yamlIMPORTANT
Use an audience that will uniquely identify the trust relationship between your AWS account and Gardener.
2. Create a policy listing the required permissions.
3. Create a role that trusts the external web identity.
In the Identity Provider dropdown menu choose the Gardener's Workload Identity Provider. 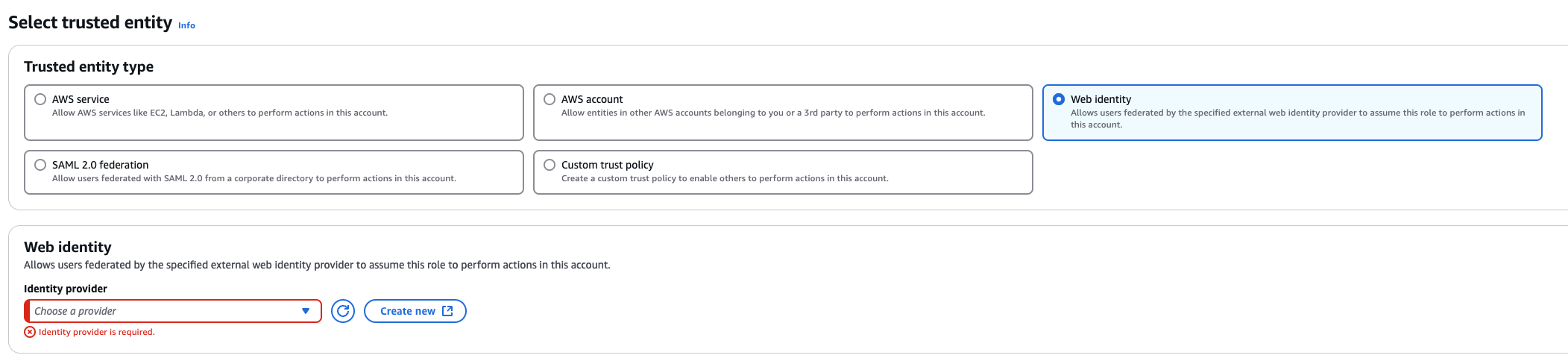
Add the newly created policy that will grant the required permissions. 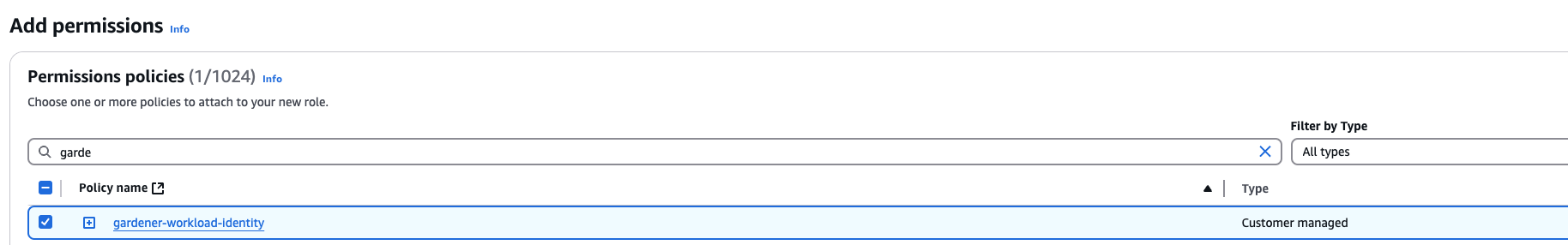
4. Configure the trust relationship.
CAUTION
Remember to reduce the scope of the identities that can assume this role only to your own controlled identities! In the example shown below WorkloadIdentitys that are created in the garden-myproj namespace and have the name aws will be authenticated and granted permissions. Later on, the scope of the trust configuration can be reduced further by replacing the wildcard "*" with the actual id of the WorkloadIdentity and converting the "StringLike" condition to "StringEquals". This is currently not possible since we do not have the id of the WorkloadIdentity yet.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:oidc-provider/example.local.gardener.cloud/garden/workload-identity/issuer"
},
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"example.local.gardener.cloud/garden/workload-identity/issuer:aud": [
"my-aws-account-gardener-workload-identity"
]
},
"StringLike": {
"example.local.gardener.cloud/garden/workload-identity/issuer:sub": "gardener.cloud:workloadidentity:garden-myproj:aws:*"
}
}
}
]
}5. Create the WorkloadIdentity in the Garden cluster.
This step will require the ARN of the role that was created in the previous step. The identity will be used by infrastructure components to authenticate against AWS APIs. A sample of such resource is shown below:
apiVersion: security.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: WorkloadIdentity
metadata:
name: aws
namespace: garden-myproj
spec:
audiences:
- my-aws-account-gardener-workload-identity
targetSystem:
type: aws
providerConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: WorkloadIdentityConfig
roleARN: arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/gardener-workload-identityTIP
Once created you can extract the whole subject of the workload identity and edit the created Role's trust relationship configuration to also include the workload identity's id. Obtain the complete sub by running the following:
SUBJECT=$(kubectl -n garden-myproj get workloadidentity aws -o=jsonpath='{.status.sub}')
echo "$SUBJECT"6. Create a CredentialsBinding referencing the AWS WorkloadIdentity and use it in your Shoot definitions.
apiVersion: security.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: CredentialsBinding
metadata:
name: aws
namespace: garden-myproj
credentialsRef:
apiVersion: security.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: WorkloadIdentity
name: aws
namespace: garden-myproj
provider:
type: awsapiVersion: core.gardener.cloud/v1beta1
kind: Shoot
metadata:
name: aws
namespace: garden-myproj
spec:
credentialsBindingName: aws
...Permissions
Please make sure that the provided credentials have the correct privileges. You can use the following AWS IAM policy document and attach it to the IAM user backed by the credentials you provided (please check the official AWS documentation as well):
Click to expand the AWS IAM policy document!
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "autoscaling:*",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ec2:*",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "elasticloadbalancing:*",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Action": [
"iam:GetInstanceProfile",
"iam:GetPolicy",
"iam:GetPolicyVersion",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:GetRolePolicy",
"iam:ListPolicyVersions",
"iam:ListRolePolicies",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:ListInstanceProfilesForRole",
"iam:CreateInstanceProfile",
"iam:CreatePolicy",
"iam:CreatePolicyVersion",
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole",
"iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy",
"iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile",
"iam:DeletePolicy",
"iam:DeletePolicyVersion",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DeleteRolePolicy",
"iam:DeleteInstanceProfile",
"iam:PutRolePolicy",
"iam:PassRole",
"iam:UpdateAssumeRolePolicy"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
},
// The following permission set is only needed, if AWS Load Balancer controller is enabled (see ControlPlaneConfig)
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cognito-idp:DescribeUserPoolClient",
"acm:ListCertificates",
"acm:DescribeCertificate",
"iam:ListServerCertificates",
"iam:GetServerCertificate",
"waf-regional:GetWebACL",
"waf-regional:GetWebACLForResource",
"waf-regional:AssociateWebACL",
"waf-regional:DisassociateWebACL",
"wafv2:GetWebACL",
"wafv2:GetWebACLForResource",
"wafv2:AssociateWebACL",
"wafv2:DisassociateWebACL",
"shield:GetSubscriptionState",
"shield:DescribeProtection",
"shield:CreateProtection",
"shield:DeleteProtection"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}InfrastructureConfig
The infrastructure configuration mainly describes how the network layout looks like in order to create the shoot worker nodes in a later step, thus, prepares everything relevant to create VMs, load balancers, volumes, etc.
An example InfrastructureConfig for the AWS extension looks as follows:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: InfrastructureConfig
enableECRAccess: true
dualStack:
enabled: false
networks:
vpc: # specify either 'id' or 'cidr'
# id: vpc-123456
cidr: 10.250.0.0/16
# gatewayEndpoints:
# - s3
zones:
- name: eu-west-1a
internal: 10.250.112.0/22
public: 10.250.96.0/22
workers: 10.250.0.0/19
# elasticIPAllocationID: eipalloc-123456
ignoreTags:
keys: # individual ignored tag keys
- SomeCustomKey
- AnotherCustomKey
keyPrefixes: # ignored tag key prefixes
- user.specific/prefix/The enableECRAccess flag specifies whether the AWS IAM role policy attached to all worker nodes of the cluster shall contain permissions to access the Elastic Container Registry of the respective AWS account. If the flag is not provided it is defaulted to true. Please note that if the iamInstanceProfile is set for a worker pool in the WorkerConfig (see below) then enableECRAccess does not have any effect. It only applies for those worker pools whose iamInstanceProfile is not set.
Click to expand the default AWS IAM policy document used for the instance profiles!
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeInstances"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
},
// Only if `.enableECRAccess` is `true`.
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:GetRepositoryPolicy",
"ecr:DescribeRepositories",
"ecr:ListImages",
"ecr:BatchGetImage"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}The dualStack.enabled flag specifies whether dual-stack or IPv4-only should be supported by the infrastructure. When the flag is set to true an Amazon provided IPv6 CIDR block will be attached to the VPC. All subnets will receive a /64 block from it and a route entry is added to the main route table to route all IPv6 traffic over the IGW.
The networks.vpc section describes whether you want to create the shoot cluster in an already existing VPC or whether to create a new one:
- If
networks.vpc.idis given then you have to specify the VPC ID of the existing VPC that was created by other means (manually, other tooling, ...). Please make sure that the VPC has attached an internet gateway - the AWS controller won't create one automatically for existing VPCs. To make sure the nodes are able to join and operate in your cluster properly, please make sure that your VPC has enabled DNS Support, explicitly the attributesenableDnsHostnamesandenableDnsSupportmust be set totrue. - If
networks.vpc.cidris given then you have to specify the VPC CIDR of a new VPC that will be created during shoot creation. You can freely choose a private CIDR range. - Either
networks.vpc.idornetworks.vpc.cidrmust be present, but not both at the same time. networks.vpc.gatewayEndpointsis optional. If specified then each item is used as service name in a corresponding Gateway VPC Endpoint.
The networks.zones section contains configuration for resources you want to create or use in availability zones. If you want to use multiple availability zones then add a second, third, ... entry to the networks.zones[] list and properly specify the AZ name in networks.zones[].name. Once an availability zone was added it cannot be removed later on. For every zone, the AWS extension creates three subnets:
- The
internalsubnet is used for internal AWS load balancers. - The
publicsubnet is used for public AWS load balancers. - The
workerssubnet is used for all shoot worker nodes, i.e., VMs which later run your applications.
For every subnet, you have to specify a CIDR range contained in the VPC CIDR specified above, or the VPC CIDR of your already existing VPC. You can freely choose these CIDRs and it is your responsibility to properly design the network layout to suit your needs.
Also, the AWS extension creates a dedicated NAT gateway for each zone. By default, it also creates a corresponding Elastic IP that it attaches to this NAT gateway and which is used for egress traffic. The elasticIPAllocationID field allows you to specify the ID of an existing Elastic IP allocation in case you want to bring your own. If provided, no new Elastic IP will be created and, instead, the Elastic IP specified by you will be used.
WARNING
If you change this field for an already existing infrastructure then it will disrupt egress traffic while AWS applies this change. The reason is that the NAT gateway must be recreated with the new Elastic IP association. Also, please note that the existing Elastic IP will be permanently deleted if it was earlier created by the AWS extension.
You can configure Gateway VPC Endpoints by adding items in the optional list networks.vpc.gatewayEndpoints. Each item in the list is used as a service name and a corresponding endpoint is created for it. All created endpoints point to the service within the cluster's region. For example, consider this (partial) shoot config:
spec:
region: eu-central-1
provider:
type: aws
infrastructureConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: InfrastructureConfig
networks:
vpc:
gatewayEndpoints:
- s3The service name of the S3 Gateway VPC Endpoint in this example is com.amazonaws.eu-central-1.s3.
Apart from the VPC and the subnets the AWS extension will also create DHCP options and an internet gateway (only if a new VPC is created), routing tables, security groups, elastic IPs, NAT gateways, EC2 key pairs, IAM roles, and IAM instance profiles.
The ignoreTags section allows to configure which resource tags on AWS resources managed by Gardener should be ignored during infrastructure reconciliation. By default, all tags that are added outside of Gardener's reconciliation will be removed during the next reconciliation. This field allows users and automation to add custom tags on AWS resources created and managed by Gardener without loosing them on the next reconciliation. Tags can be ignored either by specifying exact key values (ignoreTags.keys) or key prefixes (ignoreTags.keyPrefixes). In both cases it is forbidden to ignore the Name tag or any tag starting with kubernetes.io or gardener.cloud. Please note though, that the tags are only ignored on resources created on behalf of the Infrastructure CR (i.e. VPC, subnets, security groups, keypair, etc.), while tags on machines, volumes, etc. are not in the scope of this controller.
ControlPlaneConfig
The control plane configuration contains values for AWS-specific control plane components deployed by this extension.
An example ControlPlaneConfig for the AWS extension looks as follows:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: ControlPlaneConfig
cloudControllerManager:
# featureGates:
# SomeKubernetesFeature: true
useCustomRouteController: true
# loadBalancerController:
# enabled: true
# ingressClassName: alb
# ipamController:
# enabled: true
storage:
managedDefaultClass: falseThe cloudControllerManager.featureGates contains a map of explicitly enabled or disabled feature gates. For production usage it's not recommend to use this field at all as you can enable alpha features or disable beta/stable features, potentially impacting the cluster stability. If you don't want to configure anything for the cloudControllerManager simply omit the key in the YAML specification.
The cloudControllerManager.useCustomRouteController controls if the custom routes controller should be enabled. If enabled, it will add routes to the pod CIDRs for all nodes in the route tables for all zones.
The storage.managedDefaultClass controls if the default storage / volume snapshot classes are marked as default by Gardener. Set it to false to mark another storage / volume snapshot class as default without Gardener overwriting this change. If unset, this field defaults to true.
If the AWS Load Balancer Controller should be deployed, set loadBalancerController.enabled to true. In this case, it is assumed that an IngressClass named alb is created by the user. You can overwrite the name by setting loadBalancerController.ingressClassName. Please note: currently only the "instance" mode (alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: instance) is supported. Also, For internet-facing ALBs, AWS requires at least 2 subnets in different Availability Zones in the same VPC.
Examples for Ingress and Service managed by the AWS Load Balancer Controller:
- Prerequisites
Make sure you have created an IngressClass. For more details about parameters, please see AWS Load Balancer Controller - IngressClass
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: IngressClass
metadata:
name: alb # default name if not specified by `loadBalancerController.ingressClassName`
spec:
controller: ingress.k8s.aws/alb- Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
namespace: default
name: echoserver
annotations:
# complete set of annotations: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-load-balancer-controller/latest/guide/ingress/annotations/
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: instance # target-type "ip" NOT supported in Gardener
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: echoserver
port:
number: 80For more details see AWS Load Balancer Documentation - Ingress Specification
- Service of Type
LoadBalancer
This can be used to create a Network Load Balancer (NLB).
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
# complete set of annotations: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-load-balancer-controller/latest/guide/service/annotations/
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: instance # target-type "ip" NOT supported in Gardener
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: internet-facing
name: ingress-nginx-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
...
spec:
...
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerClass: service.k8s.aws/nlb # mandatory to be managed by AWS Load Balancer Controller (otherwise the Cloud Controller Manager will act on it)For more details see AWS Load Balancer Documentation - Network Load Balancer
WARNING
When using Network Load Balancers (NLB) as internal load balancers, it is crucial to add the annotation service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-target-group-attributes: preserve_client_ip.enabled=false. Without this annotation, if a request is routed by the NLB to the same target instance from which it originated, the client IP and destination IP will be identical. This situation, known as the hairpinning effect, will prevent the request from being processed.
WorkerConfig
The AWS extension supports encryption for volumes plus support for additional data volumes per machine. For each data volume, you have to specify a name. By default, (if not stated otherwise), all the disks (root & data volumes) are encrypted. Please make sure that your instance-type supports encryption. If your instance-type doesn't support encryption, you will have to disable encryption (which is enabled by default) by setting volume.encrpyted to false (refer below shown YAML snippet).
The following YAML is a snippet of a Shoot resource:
spec:
provider:
workers:
- name: cpu-worker
...
volume:
type: gp2
size: 20Gi
encrypted: false
dataVolumes:
- name: kubelet-dir
type: gp2
size: 25Gi
encrypted: trueNOTE
The AWS extension does not support EBS volume (root & data volumes) encryption with customer managed keys. Support for customer managed keys is out of scope for now. Only AWS managed keys is supported.
Additionally, it is possible to provide further AWS-specific values for configuring the worker pools. The additional configuration must be specified in the providerConfig field of the respective worker.
spec:
provider:
workers:
- name: cpu-worker
...
providerConfig:
# AWS worker configThe configuration will be evaluated when the provider-aws will reconcile the worker pools for the respective shoot.
An example WorkerConfig for the AWS extension looks as follows:
spec:
provider:
workers:
- name: cpu-worker
...
providerConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: WorkerConfig
volume:
iops: 10000
throughput: 200
dataVolumes:
- name: kubelet-dir
iops: 12345
throughput: 150
snapshotID: snap-1234
iamInstanceProfile: # (specify either ARN or name)
name: my-profile
instanceMetadataOptions:
httpTokens: required
httpPutResponseHopLimit: 2
# arn: my-instance-profile-arn
nodeTemplate: # (to be specified only if the node capacity would be different from cloudprofile info during runtime)
capacity:
cpu: 2 # inherited from pool's machine type if un-specified
gpu: 0 # inherited from pool's machine type if un-specified
memory: 50Gi # inherited from pool's machine type if un-specified
ephemeral-storage: 10Gi # override to specify explicit ephemeral-storage for scale fro zero
resource.com/dongle: 4 # Example of a custom, extended resource.
virtualCapacity:
subdomain.domain.com/resource-name: 1234567 # should hot update node capacity without rolloutThe .volume.iops is the number of I/O operations per second (IOPS) that the volume supports. For io1 and gp3 volume type, this represents the number of IOPS that are provisioned for the volume. For gp2 volume type, this represents the baseline performance of the volume and the rate at which the volume accumulates I/O credits for bursting. For more information about General Purpose SSD baseline performance, I/O credits, IOPS range and bursting, see Amazon EBS Volume Types (http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/EBSVolumeTypes.html) in the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud User Guide.
Constraint: IOPS should be a positive value. Validation of IOPS (i.e. whether it is allowed and is in the specified range for a particular volume type) is done on aws side.
The volume.throughput is the throughput that the volume supports, in MiB/s. As of 16th Aug 2022, this parameter is valid only for gp3 volume types and will return an error from the provider side if specified for other volume types. Its current range of throughput is from 125MiB/s to 1000 MiB/s. To know more about throughput and its range, see the official AWS documentation here.
The .dataVolumes can optionally contain configurations for the data volumes stated in the Shoot specification in the .spec.provider.workers[].dataVolumes list. The .name must match to the name of the data volume in the shoot. It is also possible to provide a snapshot ID. It allows to restore the data volume from an existing snapshot.
The iamInstanceProfile section allows to specify the IAM instance profile name xor ARN that should be used for this worker pool. If not specified, a dedicated IAM instance profile created by the infrastructure controller is used (see above).
The instanceMetadataOptions controls access to the instance metadata service (IMDS) for members of the worker. You can do the following operations:
- access IMDSv1 (default)
- access IMDSv2 -
httpPutResponseHopLimit >= 2 - access IMDSv2 only (restrict access to IMDSv1) -
httpPutResponseHopLimit >=2,httpTokens = "required" - disable access to IMDS -
httpTokens = "required"
NOTE
The accessibility of IMDS discussed in the previous point is referenced from the point of view of containers NOT running in the host network. By default on host network IMDSv2 is already enabled (but not accessible from inside the pods). It is currently not possible to create a VM with complete restriction to the IMDS service. It is however possible to restrict access from inside the pods by setting httpTokens to required and not setting httpPutResponseHopLimit (or setting it to 1).
You can find more information regarding the options in the AWS documentation.
cpuOptions grants more finegrained control over the worker's CPU configuration. It has two attributes:
coreCount: Specify a custom amount of cores the instance should be configured with.threadsPerCore: How many threads should there be on each core. Set to1to disable multi-threading.amdSevSnp: Possible values areenabledordisabled. If set toenabled, the instance will be launched with AMD SEV-SNP enabled. Only certain instance types support this feature. For more information, please refer to the AWS documentation.
Note that if you decide to configure cpuOptions both these values need to be provided. For a list of valid combinations of these values refer to the AWS documentation.
The nodeTemplate.virtualCapacity can be used to specify node extended resources that are hot-updated on nodes belonging to the pool. There are currently some caveats wrt rollouts
- If the
providerConfigsection has not yet been defined for the pool, then a rollout is un-avoidable. - If the
providerConfigis already present for the pool, thennodeTemplate.virtualCapacitycan be added without triggering a rollout as long as thevirtualCapacityis either the only element of thenodeTemplateor the last element. - If the
providerConfigis already present for the pool along with a previously definednodeTemplate.virtualCapacity, then further extended resource attributes may be freely added/modified withinvirtualCapacitywithout triggering a rollout.
Example Shoot manifest (one availability zone)
Please find below an example Shoot manifest for one availability zone:
apiVersion: core.gardener.cloud/v1beta1
kind: Shoot
metadata:
name: johndoe-aws
namespace: garden-dev
spec:
cloudProfile:
name: aws
region: eu-central-1
credentialsBindingName: core-aws
provider:
type: aws
infrastructureConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: InfrastructureConfig
networks:
vpc:
cidr: 10.250.0.0/16
zones:
- name: eu-central-1a
internal: 10.250.112.0/22
public: 10.250.96.0/22
workers: 10.250.0.0/19
elasticFileSystem:
enabled: true
controlPlaneConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: ControlPlaneConfig
workers:
- name: worker-xoluy
machine:
type: m5.large
minimum: 2
maximum: 2
volume:
size: 50Gi
type: gp2
# The following provider config is valid if the volume type is `io1`.
# providerConfig:
# apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
# kind: WorkerConfig
# volume:
# iops: 10000
zones:
- eu-central-1a
networking:
nodes: 10.250.0.0/16
type: calico
kubernetes:
version: 1.32.0
maintenance:
autoUpdate:
kubernetesVersion: true
machineImageVersion: true
addons:
kubernetesDashboard:
enabled: true
nginxIngress:
enabled: true
---
apiVersion: security.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: CredentialsBinding
metadata:
name: core-aws
namespace: garden-dev
credentialsRef:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
name: core-aws
namespace: garden-dev
provider:
type: aws
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: core-aws
namespace: garden-dev
type: Opaque
data:
accessKeyID: base64(access-key-id)
secretAccessKey: base64(secret-access-key)Example Shoot manifest (three availability zones)
Please find below an example Shoot manifest for three availability zones:
apiVersion: core.gardener.cloud/v1beta1
kind: Shoot
metadata:
name: johndoe-aws
namespace: garden-dev
spec:
cloudProfile:
name: aws
region: eu-central-1
credentialsBindingName: core-aws
provider:
type: aws
infrastructureConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: InfrastructureConfig
networks:
vpc:
cidr: 10.250.0.0/16
zones:
- name: eu-central-1a
workers: 10.250.0.0/26
public: 10.250.96.0/26
internal: 10.250.112.0/26
- name: eu-central-1b
workers: 10.250.0.64/26
public: 10.250.96.64/26
internal: 10.250.112.64/26
- name: eu-central-1c
workers: 10.250.0.128/26
public: 10.250.96.128/26
internal: 10.250.112.128/26
controlPlaneConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: ControlPlaneConfig
workers:
- name: worker-xoluy
machine:
type: m5.large
minimum: 3
maximum: 9
volume:
size: 50Gi
type: gp2
zones:
- eu-central-1a
- eu-central-1b
- eu-central-1c
networking:
nodes: 10.250.0.0/16
type: calico
kubernetes:
version: 1.32.0
maintenance:
autoUpdate:
kubernetesVersion: true
machineImageVersion: true
addons:
kubernetesDashboard:
enabled: true
nginxIngress:
enabled: trueExample Shoot manifest (IPv6)
Please find below an example Shoot manifest for an IPv6 shoot cluster:
apiVersion: core.gardener.cloud/v1beta1
kind: Shoot
metadata:
name: johndoe-aws-ipv6
namespace: garden-dev
spec:
cloudProfile:
name: aws
region: eu-central-1
credentialsBindingName: core-aws
provider:
type: aws
infrastructureConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: InfrastructureConfig
networks:
vpc:
cidr: 10.250.0.0/16
zones:
- name: eu-central-1a
public: 10.250.96.0/22
internal: 10.250.112.0/22
controlPlaneConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: ControlPlaneConfig
workers:
- ...
networking:
ipFamilies:
- IPv6
type: calico
kubernetes:
version: 1.32.0
...
addons:
kubernetesDashboard:
enabled: true
nginxIngress:
enabled: falseUse EC2 Capacity Reservations
To have your workers launch into existing Capacity Reservations, you need to add configuration about the Capacity Reservation into the workers provider-config:
spec:
provider:
workers:
- name: worker-name
...
providerConfig:
apiVersion: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/v1alpha1
kind: WorkerConfig
capacityReservation:
capacityReservationPreference: open # <open | none | capacity-reservations-only>
capacityReservationId: cr-1234abcd56example # mutually exclusive with 'capacityReservationResourceGroupArn'
capacityReservationResourceGroupArn: arn:aws:resource-groups:eu-west-2:123456789012:group/example-cr-group # mutually exclusive with 'capacityReservationId'
...Whether an instance is launched into a Capacity Reservation depends on the subset of configuration that is specified here, and also the Capacity Reservation's instance matching criteria. Some pointers:
capacityReservationPreferencegoverns the behaviour of the instance to be launched.openallows the instance to run in both Capacity Reservations and as On-Demand.capacity-reservations-onlyensures the instance will run only in Capacity Reservations (and fail otherwise) whereasnonemakes the instance run as On-Demand only.- In addition, you can target existing Capacity Reservations either explicitly by their Id, or by giving the ARN of the Capacity Reservation Resource Group they belong to. If no target is given, all open Capacity Reservations are considered.
For more information see the AWS EC2 documentation here.
The exact behaviour depends on the combination of the targeting and the reservation preferences, e.g.:
capacityReservationPreference: openwill try to launch the intance into any matching (w.r.t. instance type, platform, Availability Zone, tenancy and capacity) active Capacity Reservation in your account. This will consider only Capacity Reservations with their instance eligibility set toopen. If there are no matches, the instance is launched as On-Demand instance.capacityReservationPreference: capacity-reservations-onlywithout a target config will try to launch the instance into any matching active open Capacity Reservation in your account. If there are no matches, the launch fails.capacityReservationPreference: capacity-reservations-onlywith acapacityReservationResourceGroupArnwill try to launch the instance into an active Capacity Reservation that is part of the group and that matches the instance parameters. This will consider Capacity Reservations with their instance eligibility set toopenortargeted. If no fitting match is found in the group, the launch fails. Similarly, with acapacityReservationIdthe launch will fail if the given Capacity Reservation does not match.- Setting only a target configuration implies
capacityReservationPreference: capacity-reservations-only
NOTE
Instances without any Capacity Reservation config will launch using open targeting. They will automatically fill up any matching Capacity Reservations with open instance eligibility as they appear.
CSI volume provisioners
Every AWS shoot cluster will be deployed with the AWS EBS CSI driver. It is compatible with the legacy in-tree volume provisioner that was deprecated by the Kubernetes community and will be removed in future versions of Kubernetes. End-users might want to update their custom StorageClasses to the new ebs.csi.aws.com provisioner.
To deploy the efs-csi-driver add the elasticFileSystem section in your infrastructureConfig like in this example. This feature is only available for shoots with flow reconciler. Currently, both the controller deployment and the node daemonset will be deployed into the shoot cluster. The necessary IAM privileges will be added to the node instance profile, allowing the driver to access them via the EC2 Metadata Service. You can also use an existing elastic file system by specifying the id field in the elasticFileSystem section. However, you have to make sure that the EFS is in the same region as the shoot cluster. The section elasticFileSystem is immutable, meaning that once it is set, it cannot be changed. Important: It is not permitted to set instanceMetadataOptions to httpTokens = required while also enabling efsFileSystem. Doing so will prevent the driver from accessing the required metadata.
Node-specific Volume Limits
The Kubernetes scheduler allows configurable limit for the number of volumes that can be attached to a node. See https://k8s.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-limits/#custom-limits.
CSI drivers usually have a different procedure for configuring this custom limit. By default, the EBS CSI driver parses the machine type name and then decides the volume limit. However, this is only a rough approximation and not good enough in most cases. Specifying the volume attach limit via command line flag (--volume-attach-limit) is currently the alternative until a more sophisticated solution presents itself (dynamically discovering the maximum number of attachable volume per EC2 machine type, see also https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/aws-ebs-csi-driver/issues/347). Additional CSI flags are supported via annotations by the AWS extension:
- the
--volume-attach-limitflag of the EBS CSI driver to be configurable viaaws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/volume-attach-limitannotation on theShootresource. - the
--reserved-volume-attachmentsflag of the EBS CSI driver to be configurable viaaws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/reserved-volume-attachmentsannotation on theShootresource.
ℹ️ Please note: If the annotation is added to an existing Shoot, then reconciliation needs to be triggered manually (see Immediate reconciliation), as adding an annotation to a resource is not a change that leads to an increase of .metadata.generation in general.
Other CSI options
The newer versions of EBS CSI driver are not readily compatible with the use of XFS volumes on nodes using a kernel version <= 5.4. A workaround was added that enables the use of a "legacy XFS" mode that introduces a backwards compatible volume formating for the older kernels. You can enable this option for your shoot by annotating it with aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/legacy-xfs=true.
ℹ️ Please note: If the annotation is added to an existing Shoot, then reconciliation needs to be triggered manually (see Immediate reconciliation), as adding an annotation to a resource is not a change that leads to an increase of .metadata.generation in general.
Support for VolumeAttributesClasses (Beta in k8s 1.31)
To have the CSI-driver configured to support the necessary features for VolumeAttributesClasses on AWS for shoots with a k8s-version of at least 1.31, use the aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/enable-volume-attributes-class=true annotation on the shoot.
For more information and examples, see this markdown in the aws-ebs-csi-driver repository. Please take special note of the considerations mentioned.
Kubernetes Versions per Worker Pool
This extension supports gardener/gardener's WorkerPoolKubernetesVersion feature gate, i.e., having worker pools with overridden Kubernetes versions since gardener-extension-provider-aws@v1.34.
Shoot CA Certificate and ServiceAccount Signing Key Rotation
This extension supports gardener/gardener's ShootCARotation and ShootSARotation feature gates since gardener-extension-provider-aws@v1.36.
Flow Infrastructure Reconciler
The extension offers two different reconciler implementations for the infrastructure resource:
- terraform-based
- native Go SDK based (dubbed the "flow"-based implementation)
The default implementation currently is the terraform reconciler which uses the https://github.com/gardener/terraformer as the backend for managing the shoot's infrastructure.
The "flow" implementation is a newer implementation that is trying to solve issues we faced with managing terraform infrastructure on Kubernetes. The goal is to have more control over the reconciliation process and be able to perform fine-grained tuning over it. The implementation is completely backwards-compatible and offers a migration route from the legacy terraformer implementation.
For most users there will be no noticeable difference. However for certain use-cases, users may notice a slight deviation from the previous behavior. For example, with flow-based infrastructure users may be able to perform certain modifications to infrastructure resources without having them reconciled back by terraform. Operations that would degrade the shoot infrastructure are still expected to be reverted back.
For the time-being, to take advantage of the flow reconciler users have to "opt-in" by annotating the shoot manifest with: aws.provider.extensions.gardener.cloud/use-flow="true". For existing shoots with this annotation, the migration will take place on the next infrastructure reconciliation (on maintenance window or if other infrastructure changes are requested). The migration is not revertible.