Kube API server load balancing
Load balancing for shoot and garden Kube API servers leverages the Gardener Istio deployment.
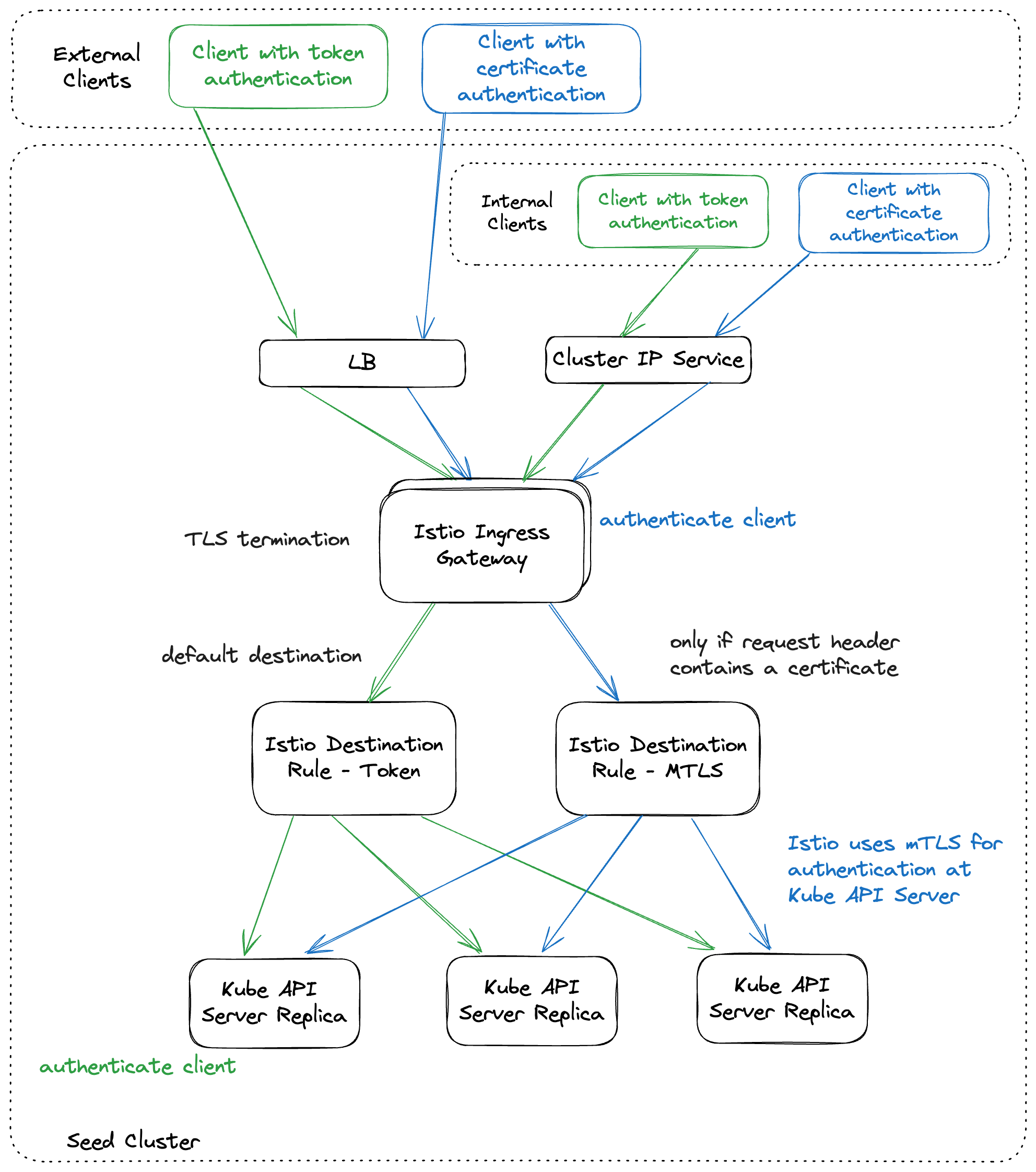
In default mode Istio performs L4 load balancing. Istio distributes connections to Kube API servers preferably in the same zone (Topology-Aware Traffic Routing). Requests are not taken into account for a load balancing decisions. TLS is terminated by Kube API server instances.
There is a second mode which can be activated via IstioTLSTermination feature gate in gardenlet and gardener-operator. This mode introduces L7 load balancing and distributes requests among the Kube API server instances. It does not use Topology-Aware Traffic Routing since it contradicts the load balancing goal. In this mode TLS is terminated in Istio. However, Istio creates a TLS connection to Kube API servers, too, so the traffic within the cluster remains encrypted.
This document is focused on the second mode.
On seeds where the feature gate is activated L7 load balancing can still be deactivated for single shoots by annotating them with shoot.gardener.cloud/disable-istio-tls-termination: "true".
How it works
L7 load balancing works for the externally resolvable Kube API server endpoints, for connections which use apiserver-proxy like endpoint kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local and for control plane components running in shoot namespaces.
Clients might authenticate at Kube API server using client certificates, tokens or might connect unauthenticated. In the first case Istio ingress gateway must validate client certificates because it terminates the TLS connection. Thus, it is configured with an optional mutual TLS authentication. It is optional because in case of the authentication via token, the token is validated by Kube API server. Unauthenticated requests are handled by Kube API server too. For TLS termination and client certificate validation Kube API server certificate (including the private key) and the client CA bundle must be synchronized into the namespace where istio ingress gateway is running.
While token authentication and unauthenticated requests are still handled by Kube API server itself, it requires dedicated request headers if an authentication proxy is used. Based on these headers Kube API server identifies the user and group of a request. They are added with a lua script running in an envoy filter in istio ingress gateway. Kube API server trusts the headers set by the authentication proxy so it requires an mTLS connection to the proxy. Istio uses the front proxy CA (including private key) and the server CA bundle to establish the mTLS connection. These secrets again must be synchronized into the namespace where istio ingress gateway is running. There is an own istio destination rule for the mTLS connection.
The destination host of the istio virtual service has an istio destination rule which does not use mTLS so that Kube API server authenticates requests by itself. It is used for the token based authentication. The istio destination rule for the mTLS connection is set by the lua script mentioned above only. This is a safety net to prevent that requests can reach Kube API server via the trusted connection in case the lua scripts fails for some reason.
Cluster internal control plane components like kube-controller-manager, kube-scheduler and gardener-resource-manager use L7 load balancing too. They connect to the Kube API server via a cluster IP service for istio ingress gateway. The generic token kubeconfig uses the public Kube API server endpoint. In order to avoid external traffic, the control plane components use host aliases in their pod specifications. For convenience, the host aliases are automatically added by the pod-kube-apiserver-load-balancing webhook in gardener-resource-manager. It also adds a label to create a network policy allowing egress traffic to the istio ingress gateway pods. This works for control plane components running in shoot namespaces and for the virtual garden control plane.
The flow for L7 load balancing is shown in the following illustration.