Deploying Gardener Locally and Enabling Provider-Extensions
This document will walk you through deploying Gardener on your local machine and bootstrapping your own seed clusters on an existing Kubernetes cluster. It is supposed to run your local Gardener developments on a real infrastructure. For running Gardener only entirely local, please check the getting started locally documentation. If you encounter difficulties, please open an issue so that we can make this process easier.
Overview
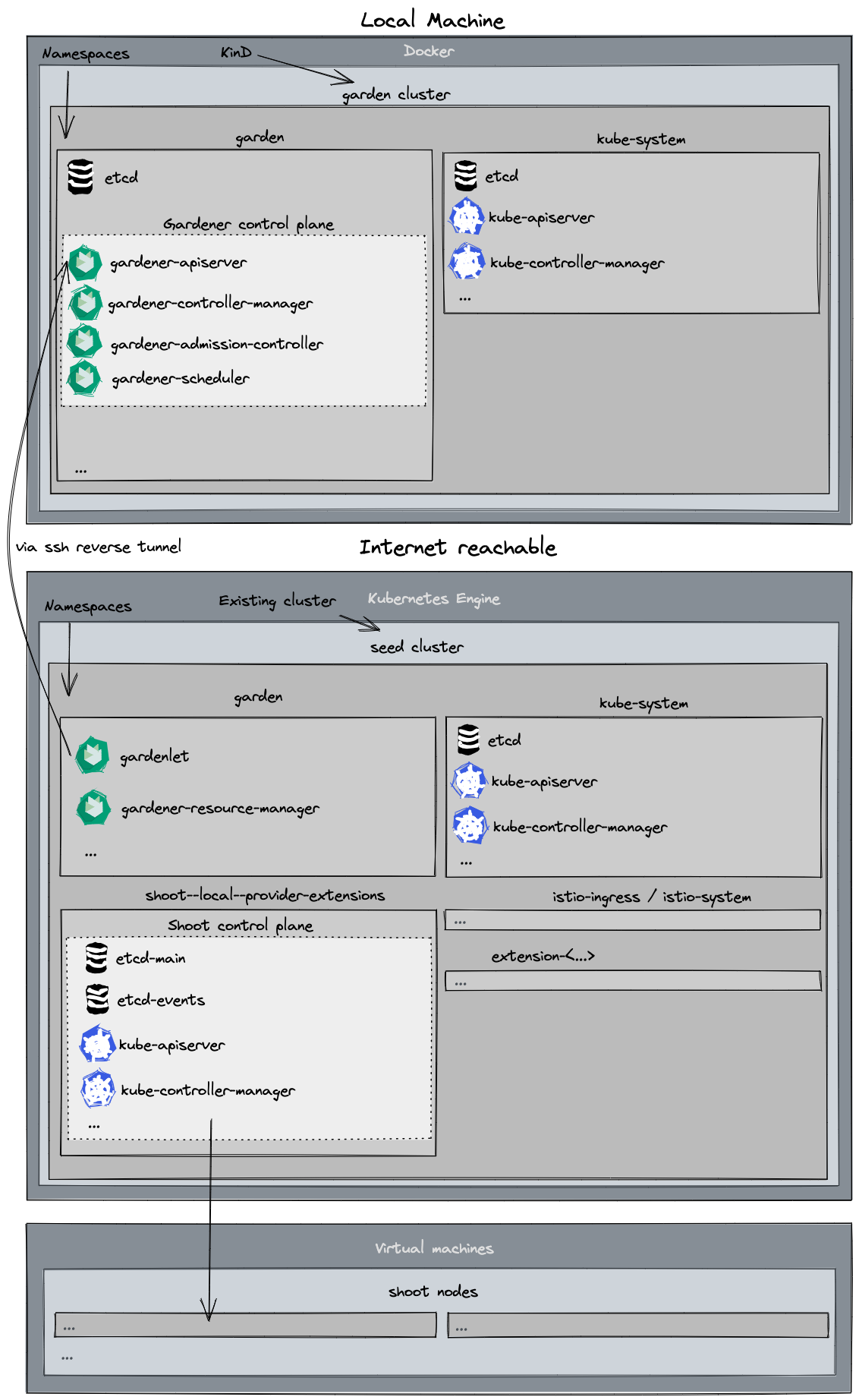
Gardener runs in any Kubernetes cluster. In this guide, we will start a KinD cluster which is used as garden cluster. Any Kubernetes cluster could be used as seed clusters in order to support provider extensions (please refer to the architecture overview). This guide is tested for using Kubernetes clusters provided by Gardener, AWS, Azure, and GCP as seed so far.
Based on Skaffold, the container images for all required components will be built and deployed into the clusters (via their Helm charts).
Prerequisites
- Make sure that you have followed the Local Setup guide up until the Get the sources step.
- Make sure your Docker daemon is up-to-date, up and running and has enough resources (at least
8CPUs and8Gimemory; see the Docker documentation for how to configure the resources for Docker for Mac).Additionally, please configure at least
120Giof disk size for the Docker daemon. Tip: You can clean up unused data withdocker system dfanddocker system prune -a. - Make sure that you have access to a Kubernetes cluster you can use as a seed cluster in this setup.
- The seed cluster requires at least 16 CPUs in total to run one shoot cluster
- You could use any Kubernetes cluster for your seed cluster. However, using a Gardener shoot cluster for your seed simplifies some configuration steps.
- When bootstrapping
gardenletto the cluster, your new seed will have the same provider type as the shoot cluster you use - an AWS shoot will become an AWS seed, a GCP shoot will become a GCP seed, etc. (only relevant when using a Gardener shoot as seed).
Provide Infrastructure Credentials and Configuration
As this setup is running on a real infrastructure, you have to provide credentials for DNS, the infrastructure, and the kubeconfig for the Kubernetes cluster you want to use as seed.
CAUTION
There are .gitignore entries for all files and directories which include credentials. Nevertheless, please double check and make sure that credentials are not committed to the version control system.
DNS
Gardener control plane requires DNS for default and internal domains. Thus, you have to configure a valid DNS provider credentials for your setup.
- In case DNS credentials based on workload identities are used,
WorkloadIdentitys should be maintained at/example/provider-extensions/garden/controlplane/domain-workload-identities.yaml. - If static DNS credentials are used, the
Secrets should be maintained at/example/provider-extensions/garden/controlplane/domain-secrets.yaml.
There are templates with .tmpl suffixes for the files in the corresponding folders.
Infrastructure
In case infrastructure credentials based on workload identities are used, WorkloadIdentitys and the corresponding CredentialsBindings should be maintained at:
/example/provider-extensions/garden/project/with-workload-identity/credentials/infrastructure-workloadidentities.yaml/example/provider-extensions/garden/project/with-workload-identity/credentials/credentialsbindings.yaml
If static credentials are used, the Secrets and the corresponding CredentialsBindings that reference the Secrets should be maintained at:
/example/provider-extensions/garden/project/without-workload-identity/credentials/infrastructure-secrets.yaml/example/provider-extensions/garden/project/without-workload-identity/credentials/credentialsbindings.yaml
There are templates with .tmpl suffixes for the files in the corresponding folders.
Projects
The projects and the namespaces associated with them should be maintained at /example/provider-extensions/garden/project/base/project.yaml.
You can find a template for the file at /example/provider-extensions/garden/project/base/project.yaml.tmpl.
Seed Cluster Preparation
The kubeconfig of your Kubernetes cluster you would like to use as seed should be placed at /example/provider-extensions/seed/kubeconfig. Additionally, please maintain the configuration of your seed in /example/provider-extensions/gardenlet/values.yaml. It is automatically copied from values.yaml.tmpl in the same directory when you run make gardener-extensions-up for the first time. It also includes explanations of the properties you should set.
Using a Gardener Shoot cluster as seed simplifies the process, because some configuration options can be taken from shoot-info and creating DNS entries and TLS certificates is automated.
However, you can use different Kubernetes clusters for your seed too and configure these things manually. Please configure the options of /example/provider-extensions/gardenlet/values.yaml upfront. For configuring DNS and TLS certificates, make gardener-extensions-up, which is explained later, will pause and tell you what to do.
External Controllers
You might plan to deploy and register external controllers for networking, operating system, providers, etc. Please put ControllerDeployments and ControllerRegistrations into the /example/provider-extensions/garden/controllerregistrations directory. The whole content of this folder will be applied to your Garden cluster.
CloudProfiles
There are no demo CloudProfiles yet. Thus, please copy CloudProfiles from another landscape to the /example/provider-extensions/garden/cloudprofiles directory or create your own CloudProfiles based on the gardener examples. Please check the GitHub repository of your desired provider-extension. Most of them include example CloudProfiles. All files you place in this folder will be applied to your Garden cluster.
Setting Up the KinD Cluster
First, you will need to add
127.0.0.1 registry.local.gardener.cloudto your /etc/hosts.
make kind-extensions-upThis command sets up a new KinD cluster named gardener-extensions and stores the kubeconfig in the /example/gardener-local/kind/extensions/kubeconfig file.
It might be helpful to copy this file to
$HOME/.kube/config, since you will need to target this KinD cluster multiple times. Alternatively, make sure to set yourKUBECONFIGenvironment variable to/example/gardener-local/kind/extensions/kubeconfigfor all future steps viaexport KUBECONFIG=$PWD/example/gardener-local/kind/extensions/kubeconfig.
All of the following steps assume that you are using this kubeconfig.
Additionally, this command deploys a local container registry to the cluster as well as a few registry mirrors that are set up as a pull-through cache for all upstream registries Gardener uses by default. This is done to speed up image pulls across local clusters.
The local registry can now be accessed either via localhost:5001 or registry.local.gardener.cloud:5001 for pushing and pulling. The storage directories of the registries are mounted to your machine under dev/local-registry. With this, mirrored images don't have to be pulled again after recreating the cluster.
The command also deploys a default calico installation as the cluster's CNI implementation with NetworkPolicy support (the default kindnet CNI doesn't provide NetworkPolicy support). Furthermore, it deploys the metrics-server in order to support HPA and VPA on the seed cluster.
Setting Up Gardener (Garden on KinD, Seed on Gardener Cluster)
make gardener-extensions-upThis will first prepare the basic configuration of your KinD and Gardener clusters. Afterwards, the images for the Garden cluster are built and deployed into the KinD cluster. Finally, the images for the Seed cluster are built, pushed to a container registry on the Seed, and the gardenlet is started.
If support for workload identity is required you can invoke the top command with DEV_SETUP_WITH_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_SUPPORT variable set to true. This will cause the Gardener Discovery Server to be deployed and exposed through the seed cluster. External systems can be then configured to trust the workload identity issuer of the local Garden cluster.
DEV_SETUP_WITH_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_SUPPORT=true make gardener-extensions-upIMPORTANT
The Gardener Discovery Server is started with a token which is valid for 48 hours. Rerun DEV_SETUP_WITH_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_SUPPORT=true make gardener-extensions-up in order to renew the token.
When working with multiple seed clusters you need to only pass DEV_SETUP_WITH_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_SUPPORT=true for the one seed cluster that will be used to expose the workload identity documents. A single Garden cluster needs only one Gardener Discovery Server.
To setup workload identity with your provider please refer to the provider extension specific docs:
Adding Additional Seeds
Additional seed(s) can be added by running
make gardener-extensions-up SEED_NAME=<seed-name>The seed cluster preparations are similar to the first seed:
The kubeconfig of your Kubernetes cluster you would like to use as seed should be placed at ./example/provider-extensions/seed/kubeconfig-<seed-name>. Additionally, please maintain the configuration of your seed in ./example/provider-extensions/gardenlet/values-<seed-name>.yaml. It is automatically copied from values.yaml.tmpl in the same directory when you run make gardener-extensions-up SEED_NAME=<seed-name> for the first time. It also includes explanations of the properties you should set.
Removing a Seed
If you have multiple seeds and want to remove one, just use
make gardener-extensions-down SEED_NAME=<seed-name>If it is not the last seed, this command will only remove the seed, but leave the local Gardener cluster and the other seeds untouched. To remove all seeds and to clean up the local Gardener cluster, you have to run the command for each seed.
TIP
If using development setup that supports workload identity pass DEV_SETUP_WITH_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_SUPPORT=true when removing the seed that was used to host the Gardener Discovery Server.
DEV_SETUP_WITH_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_SUPPORT=true make gardener-extensions-down SEED_NAME=<seed-name>Rotate credentials of container image registry in a Seed
There is a container image registry in each Seed cluster where Gardener images required for the Seed and the Shoot nodes are pushed to. This registry is password protected. The password is generated when the Seed is deployed via make gardener-extensions-up. Afterward, it is not rotated automatically. Otherwise, this could break the update of gardener-node-agent, because it might not be able to pull its own new image anymore. This is no general issue of gardener-node-agent, but a limitation provider-extensions setup. Gardener does not support protected container images out of the box. The function was added for this scenario only.
However, if you want to rotate the credentials for any reason, there are two options for it.
- run
make gardener-extensions-up(to ensure that your images are up-to-date) reconcileall shoots on the seed where you want to rotate the registry password- run
kubectl delete secrets -n registry registry-passwordon your seed cluster - run
make gardener-extensions-up reconcilethe shoots again
or
reconcileall shoots on the seed where you want to rotate the registry password- run
kubectl delete secrets -n registry registry-passwordon your seed cluster - run
./example/provider-extensions/registry-seed/deploy-registry.sh <path to seed kubeconfig> <seed registry hostname> reconcilethe shoots again
Pause and Unpause the KinD Cluster
The KinD cluster can be paused by stopping and keeping its docker container. This can be done by running:
make kind-extensions-downWhen you run make kind-extensions-up again, you will start the docker container with your previous Gardener configuration again.
This provides the option to switch off your local KinD cluster fast without leaving orphaned infrastructure elements behind.
Creating a Shoot Cluster
You can wait for the Seed to be ready by running:
kubectl wait --for=condition=gardenletready seed provider-extensions --timeout=5mmake kind-extensions-up already includes such a check. However, it might be useful when you wake up your Seed from hibernation or unpause you KinD cluster.
Alternatively, you can run kubectl get seed provider-extensions and wait for the STATUS to indicate readiness:
NAME STATUS PROVIDER REGION AGE VERSION K8S VERSION
provider-extensions Ready gcp europe-west1 111m v1.61.0-dev v1.24.7In order to create a first shoot cluster, please create your own Shoot definition and apply it to your KinD cluster. gardener-scheduler includes candidateDeterminationStrategy: MinimalDistance configuration so you are able to run schedule Shoots of different providers on your Seed.
You can wait for your Shoots to be ready by running kubectl -n garden-local get shoots and wait for the LAST OPERATION to reach 100%. The output depends on your Shoot definition. This is an example output:
NAME CLOUDPROFILE PROVIDER REGION K8S VERSION HIBERNATION LAST OPERATION STATUS AGE
aws aws aws eu-west-1 1.24.3 Awake Create Processing (43%) healthy 84s
aws-arm64 aws aws eu-west-1 1.24.3 Awake Create Processing (43%) healthy 65s
azure az azure westeurope 1.24.2 Awake Create Processing (43%) healthy 57s
gcp gcp gcp europe-west1 1.24.3 Awake Create Processing (43%) healthy 94sAccessing the Shoot Cluster
Your shoot clusters will have a public DNS entries for their API servers, so that they could be reached via the Internet via kubectl after you have created their kubeconfig.
We encourage you to use the adminkubeconfig subresource for accessing your shoot cluster. You can find an example how to use it in Accessing Shoot Clusters.
Deleting the Shoot Clusters
Before tearing down your environment, you have to delete your shoot clusters. This is highly recommended because otherwise you would leave orphaned items on your infrastructure accounts.
./hack/usage/delete shoot <your-shoot> garden-localTear Down the Gardener Environment
Before you delete your local KinD cluster, you should shut down your Shoots and Seed in a clean way to avoid orphaned infrastructure elements in your projects.
Please ensure that your KinD and Seed clusters are online (not paused or hibernated) and run:
make gardener-extensions-downThis will delete all Shoots first (this could take a couple of minutes), then uninstall gardenlet from the Seed and the gardener components from the KinD. Finally, the additional components like container registry, etc., are deleted from both clusters.
When this is done, you can securely delete your local KinD cluster by running:
make kind-extensions-clean